Education Loan is a complex concept for most of the students and parents. There are many confusions and misconceptions and because this is about education and most importantly about the future of the students, these should be clarified beforehand.
In this Detailed Guide on Student Loan for abroad studies, you we Learn:
Let's start.

India is a young nation with over 35 million students enrolled in higher education in FY19. Following the pandemic, the Indian education system had faced several obstacles but had seen growth in the number of students enrolling in higher education. Despite the world now transitioning to online teaching, the cost of education has risen.
To cover the exorbitant costs of higher education, many students have no choice but to take education loans for abroad studies. According to a report published in Economic times, despite the pandemic, the number of people opting for education loans increased highly and made a new high.
This article aims to familiarize you with all the fundamental yet important concepts related to education loans. To know the subject in detail, you can read the articles given below each section (which we’d encourage you to do) that goes into great detail about the subject.
An education loan is a loan that students seek to help them fulfill the financial obligations of their education, whether it be in India or overseas. It may be used for undergraduate, postgraduate, and professional degree/diploma courses in engineering, management, and other subjects. Education loans cover not just tuition fees but also living expenses along with travel fares, books, laptops (if required for education), and all education-related costs.
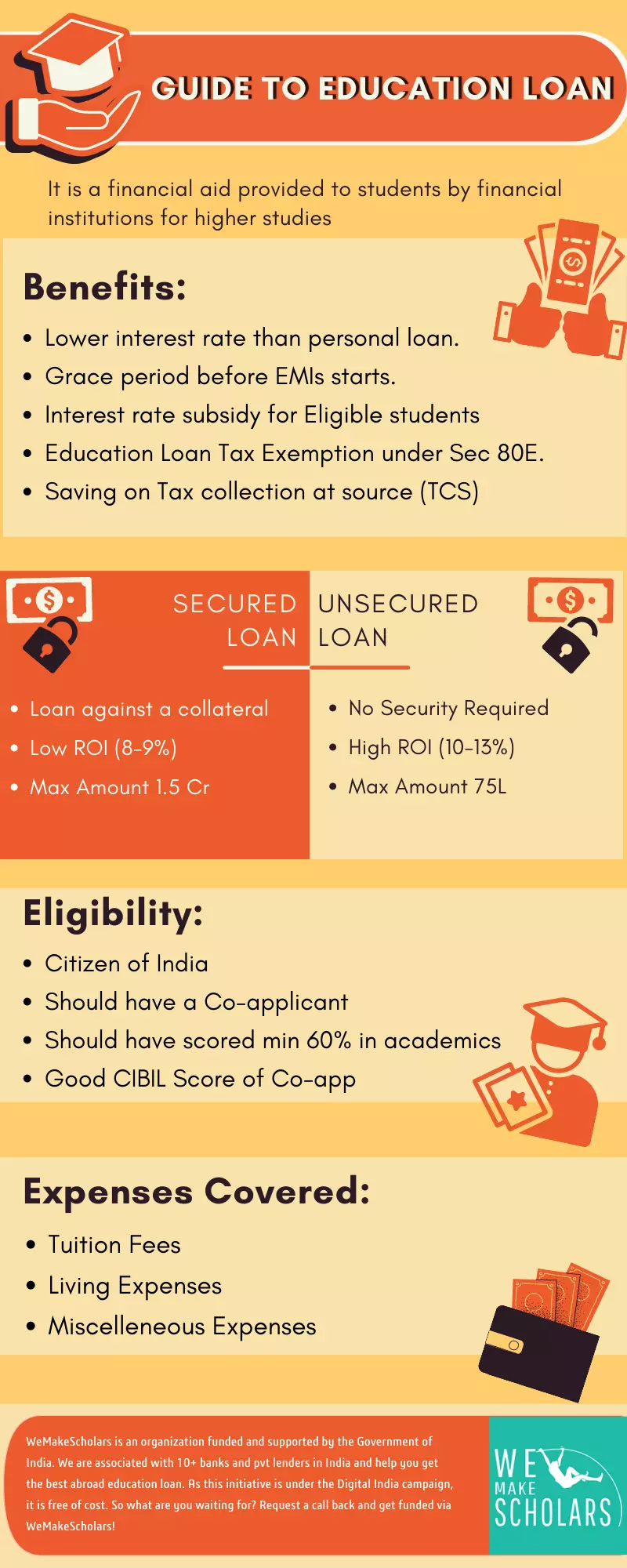
The first and most important thing to understand is that students can choose between two types of student loans: collateral and non-collateral education loans.
To get a secured/collateral loan, students are required to pledge collateral as security to take a loan against it. The collateral is of two types-
A student can also receive an education loan using the property of a relative or friend who is ready to put up their property as collateral.
There are further classifications for what all kinds of immovable property are not accepted as security, as well as which types of collateral are given priority, and so on. For further detail about the importance and benefits of having collateral in an education loan, you can read the article- Collateral Education Loan which has covered this subject thoroughly.
A non-collateral loan is one that does not require any form of collateral. Rather than depending on collateral as security, lenders verify students' creditworthiness based on eligibility parameters specified by them.
Unsecured education loans are for students who don't have any collateral or don't want to put up collateral (for any reason) for education loans. This is considered to be an expensive loan when compared to a collateral education loan.
Now that you know that there are two types of education loans, the next step is to know who the lenders are. The education loans are provided by
Whether or not you are getting a fair deal on an education loan is partly determined by the lender from whom you are borrowing the education loan.
The private sector banks, NBFCs, and international lenders are all private lenders. Click on the link to understand the difference between public and private lenders and which ones are the best for your abroad education loans.
These aforementioned lending institutions provide several education loan schemes tailored to cater to students with varying needs. Education loan schemes could be based on -
What varies with different education loan schemes from different lending institutions are the interest rates, maximum loan limit, loan margin, moratorium period, etc.
Know about the best schemes for abroad education loans provided by various prominent banks in this latest article-
The country wherein students pursue their studies is important to lenders, particularly private lenders. The public sector banks on the other hand do not bother much as they pretty much fund all courses in almost every major country with a reputation for education.
The primary reason private lenders are so particular about countries is that, unlike government banks, they generally issue non-collateralized study loans to students. And in order to ensure their funding and returns, private lenders finance education in countries with a well-regarded educational system and better employment prospects for students.
The following are the major countries for which private lenders provide funding:
Sometimes, depending on case to case basis, good-ranked universities in other countries may also be accepted by private lenders for funding.
The process for obtaining an education loan is different for both types of loans and lenders. Ideally, students prefer to take secured and unsecured education loans from public and private lenders respectively.
So, we have basically two student loan procedures-
And so, when you go through our in depth article on education loan procedure in India, you'll discover each step involved in a secured and unsecured education loan procedure for abroad studies. Knowing these steps beforehand will help you in your decision-making during your education loan process.
Now, it is patently obvious that lenders do not simply hand out education loans to any student, there are certain criteria that students must meet in order to be considered eligible for education loans. Eligibility criteria may vary from bank to bank as per the type of loan you opt for.
More often than not, the majority of the education loan applications are turned down by lending institutions because the students or their co-applicant do not meet the eligibility requirements set by them.
The official sites of multiple lenders will have these below-given eligibilities in common-
There are other unmentioned eligibility criteria for education loans like the importance of a good CIBIL score, Gap check, country, university, financial co-applicants profile, etc, which you should know before your loan process.
The qualifying requirements of various lending institutions have been fully described in this article-
Education loan eligibility in India 2021-22 [Complete Guide].
A co-applicant/ co-borrower/ co-signer is a member of your family (ideally your parents) who joins the loan application and bears responsibility for repayment if for any reason you couldn’t. And also for banks to have someone here in India to contact for any due diligence while the student is abroad.
It is a must that you have to have a co-applicant for your education loan procedure. Not everyone from the family can be a co-applicant because there are certain eligibility criteria for co-applicant set by lenders. The income of your co-applicant doesn't matter for a collateralized loan from government banks. However, as with private lenders (except international lenders), the income of a co-applicant is of great importance as they are required to initially pay the accrued interest during the moratorium period.
When it comes to getting an education loan, there are several stages to follow, one of which is paperwork. Your student loan process will not begin until you have provided all of the required documents (either online or in-person at the bank's branch). This documentation process is important for the lenders to verify the applicant's credibility.
The following is a list of required education loan documents that you must provide to banks when applying for a loan:
Based on the loan type, there will be collateral-related documents for a collateral education loan and additional co-applicant's documents for a non-collateral education loan.
As already said, students prefer taking a secured and unsecured education loan from Government and private lenders respectively, and so you can find out the Education loan documents required by Government and private banks by going through the article.
When taking out student loans, the first thing students look for is the interest rates, since even a 0.5 percent variation in interest rates may have a considerable impact on students in the long run.
The education loan interest rates offered by private lenders are subject to how good the students' profile is. Despite this, the interest rates offered by government banks are at least 2-3% lower than that of private lenders.
| Government bank | 8-9% |
|---|---|
| Private banks | 10% and above |
| NBFCs | 11-13.5% |
| International lenders | 12-15% (converted from LIBOR to MCLR) |
To know the actual interest rates offered by different banks and NBFCs, refer to this article which gets updated on a regular basis-
Education loan interest rates Comparison between public and private sector banks in India.
EMI (Equated monthly installment) is a monthly payment made by students to their lending institutions where they pay back the money they borrowed for their education, plus interest.
Using an EMI calculator will help you figure out your loan expenses and the amount you have to pay monthly depending on an individual’s income and financial stability.
The EMI calculator is simple to use. Just visit the Education loan EMI calculator, fill up the details and calculate your EMI on an abroad student loan.
A loan margin is the percentage of money paid by students toward their overall expenditures. Public-sector banks are the most likely to follow it, with a loan margin of a minimum of 10%.
For eg., if a bank sets their loan margin at 10%, that means the education loan from the bank will cover 90% of your entire expenditures, and the rest 10% is expected to be paid by you. You must first pay your share of the money to the banks, who will then transfer the funds to the students.
A 0% loan margin is offered by private lenders on unsecured education loans. Furthermore, depending on specific criteria, certain public-sector banks provide a 0% loan margin on a secured education loan as well.
The loan margin is in itself a bit broad and complex topic, which has been extensively covered in this article-
Once you had gone through the entire education loan process, selected the type of loan from a lender, submitted documents, deemed eligible, and got the offer (amount, interest rates, etc) from the lender, you had to pay the processing fee and get the sanction letter.
An education loan sanction letter includes the basic information about the education loan( loan amount, interest rate, borrower’s name, loan tenure) and other terms and conditions. It is proof that the student has applied for and been approved for the loan.
Your sanction letter stays valid for 6 months, which means you had to take your first disbursement within 6 months from the day of its issuance.
But don't stay under the impression that the funding process is over just yet, there are several issues faced by students even after the loan is sanctioned. You can read about the issues and their solutions here- Issues to expect after your loan is sanctioned-education loan sanction issues.
The transfer of education loan funds (any amount from sanctioned loan amount) from the lender to the borrower’s concerned account (Fee to university and rest to the student) is referred to as 'disbursement'. The disbursement procedure in different banks and for different countries is different.
For a select few countries, the disbursement procedure is critical to the visa application process. Students have to fulfill the financial obligations through pre-visa disbursement (tuition fee, living expenses) before getting their student visa in time. For eg, - GIC for Canada, I-20 for the USA, Blocked account for Germany, etc.
To know the prerequisites before disbursement, the actual disbursement process in different lenders, or any disbursement related query, read this post that will provide you with further detailed information- Education Loan Disbursement Process in Government Banks and NBFCs.
A moratorium period is defined as a gap in the repayment tenure of the loan where students are not obliged to pay the loan EMIs during the period. The moratorium period consists of your course duration plus 6-12 months. All public-sector banks have an obligation to grant the moratorium period to students.
While public-sector banks allow you to pay nothing during the moratorium period, private lenders require you to pay either partial or full interest during the period.
The fact that an education loan has a moratorium period distinguishes it from other types of loans.
A repayment period begins once you start paying either interest or direct EMIs to the lending bank. Your moratorium period may or may not come under a repayment period depending on whether you are paying anything during the period to the bank or not.
The education loan repayment process is greatly dependent on the policies set by different lenders.
Usually, lending institutions provide up to 15 years to students to repay their loans, although students can pay off their loans sooner if they can.
Education loan transfer or refinance is a process wherein you can transfer your loan from one bank to another. The reason behind transferring could be for
The reason behind the majority of the education loan transfer is for lower interest rates from a private lender to a public bank.
It is to be noted that when an unsecured education loan from a private lender is being transferred to a public bank, the collateral must be pledged if the loan amount that is being transferred is more than 7.5 lakhs.
There are certain terms and conditions before you can transfer your education loan, read about the subject in detail here-
All you need to know about Education Loan Transfer in India.
To lighten the financial load of the students from economically backward sections, the Indian government has introduced some education loan interest subsidy schemes where the interest portion for the entire moratorium period is paid off by the government.
Below are the three major interest rate subsidy schemes provided by the Indian Government banks-
Through these subsidy schemes, eligible students can save an amount of up to 6 Lakhs from their entire repayable loan amount.
To know in detail about the education loan interest rate subsidy schemes like eligibility requirement to avail these schemes, how much you can get, what are the process and all, read here- Education Loan Interest Subsidy: Government schemes to know.
Now that everyone who is qualified for subsidy schemes can take advantage of them, what about those who aren't?
So under section 80E of the Income Tax Act, 1961 - education loan tax exemption policy, the interest paid on the educational loan can be claimed as a deduction. This deduction can be claimed by either you or your co-applicant.
Bear in mind, education loan tax exemption can only be claimed once the repayment commences. It can only be claimed for higher studies and only if an education loan is taken from Indian lending institutions (Public and Private banks).
Through this article, we've already established multiple benefits as to why you should opt for an education loan for your education.
To know more benefits of education loans, read this article-
So, while we've gone through the education loan concepts in order to help you understand them better, you may still have some questions, which we've attempted to answer through the articles listed below.
Ans. Yes, if not for education loans, millions of students would never have made it to their dream careers since we all know how important education is. Opting for an education loan provides numerous benefits like lower interest rates compared to personal loans, payment-free moratorium periods, tax rebate under section 80E, savings on tax collection at source, etc.
Ans. Government banks are considered to be a more suitable alternative for education loans because the overall deal you get from government banks is better compared to that of private lenders. The interest rates are lower, a larger loan amount, a no-payment moratorium period with a longer repayment period, and so on.
Ans. Not necessarily, you can also opt for a non-collateral education loan where you need not pledge any property. But lenders have a few eligibility criteria set for non-collateral education loans. Ideally, it is advised to opt for a collateral education loan from government banks for a lower interest rate by pledging the property (House, Flat, Non-agricultural land, FD, Term insurances policies, etc).